Estimated reading time 10 minutes, 20 seconds.
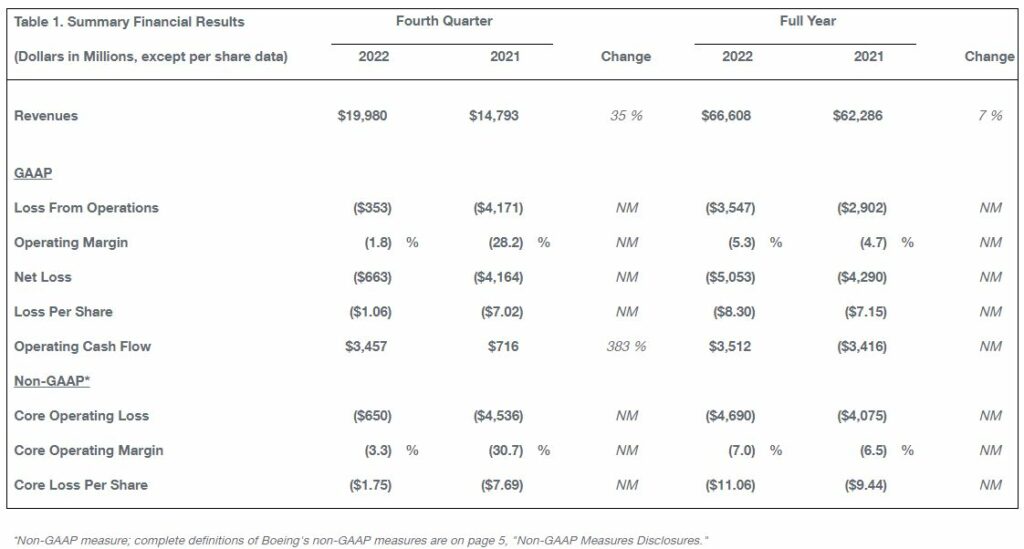
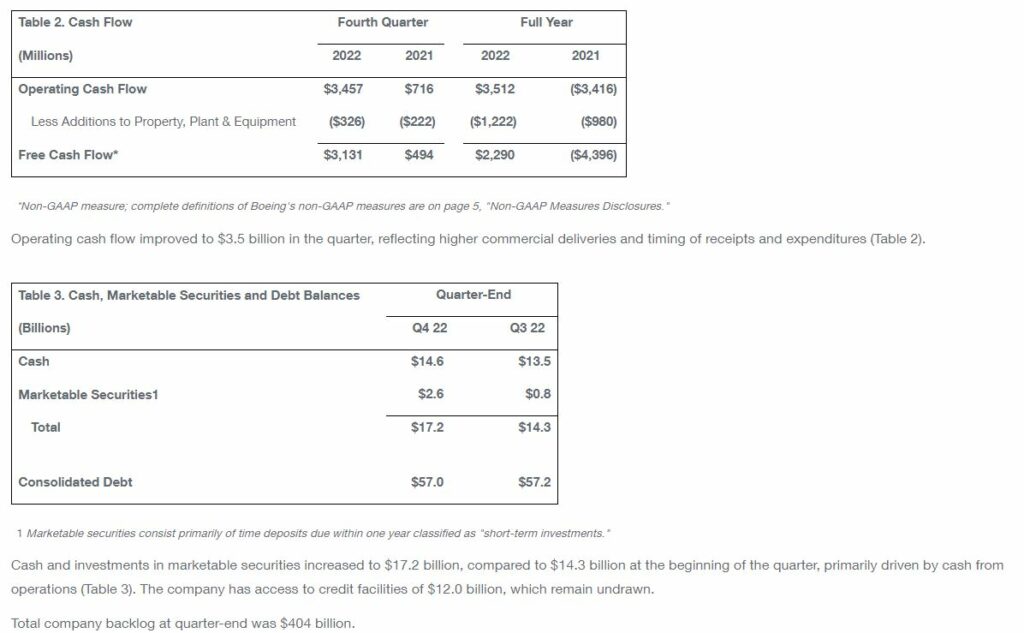
The Boeing Company [NYSE: BA] recorded fourth-quarter revenue of $20.0 billion, GAAP loss per share of ($1.06), and core loss per share (non-GAAP)* of ($1.75) (Table 1). Boeing also generated $3.5 billion of operating cash flow and $3.1 billion of free cash flow (non-GAAP). Results improved on commercial volume and performance.

“We had a solid fourth quarter, and 2022 proved to be an important year in our recovery,” said Dave Calhoun, Boeing President and Chief Executive Officer. “Demand across our portfolio is strong, and we remain focused on driving stability in our operations and within the supply chain to meet our commitments in 2023 and beyond. We are investing in our business, innovating and prioritizing safety, quality and transparency in all that we do. While challenges remain, we are well positioned and are on the right path to restoring our operational and financial strength.”
Segment Results
Commercial Airplanes
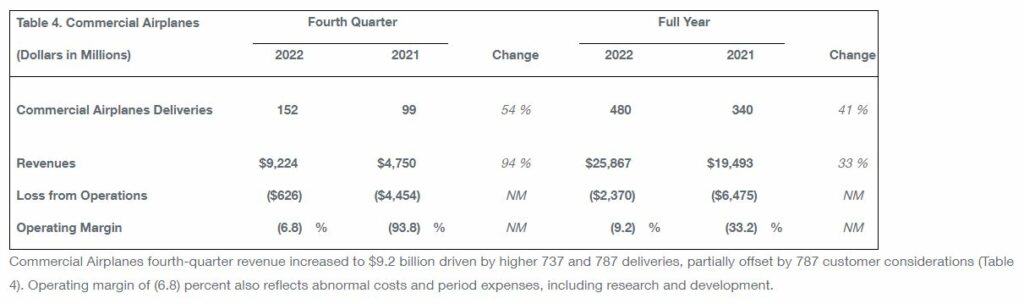
The 737 program is stabilizing production rate at 31 per month with plans to ramp production to approximately 50 per month in the 2025/2026 timeframe. Additionally, the 787 program continues at a low production rate with plans to ramp production to five per month in late 2023 and to 10 per month in the 2025/2026 timeframe.
During the quarter, the company secured net orders for 376 aircraft, including an order from United Airlines for 100 737 MAX and 100 787 airplanes. Commercial Airplanes delivered 152 airplanes during the quarter and backlog included over 4,500 airplanes valued at $330 billion.
Defense, Space & Security
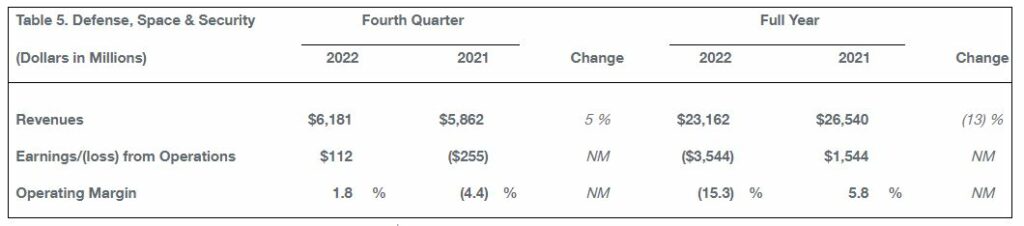
Defense, Space & Security fourth-quarter revenue was $6.2 billion. Fourth-quarter operating margin of 1.8 percent reflects the continued operational impact of labor instability and supply chain disruption.
Defense, Space & Security delivered 45 aircraft and three satellites, including the first P-8A Poseidon to New Zealand. Also in the quarter, the Boeing-built Space Launch System core stage powered the first Artemis I mission to the moon and the T-7A program completed engine testing.
During the quarter, Defense, Space & Security captured awards from Japan for two KC-46A Tankers and from the Egyptian Air Force for 12 CH-47F Chinook helicopters. Backlog at Defense, Space & Security was $54 billion, of which 28 percent represents orders from customers outside the U.S.
Global Services
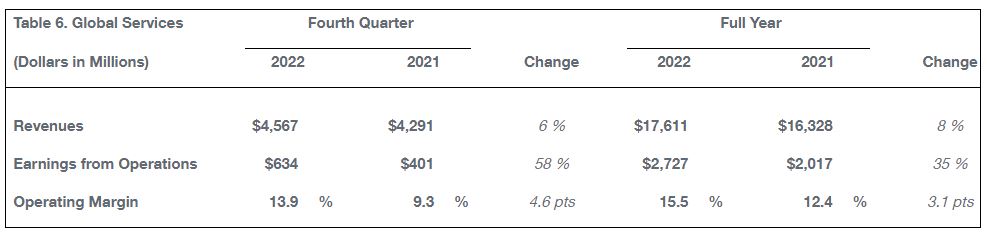
Global Services fourth-quarter revenue of $4.6 billion and operating margin of 13.9 percent reflect higher commercial volume, partially offset by lower government volume.
During the quarter, Global Services finalized the U.S. Air Force F-15 depot support order and opened the Germany Distribution Center to serve 6,000+ customers with chemicals and specialty materials.
Additional Financial Information
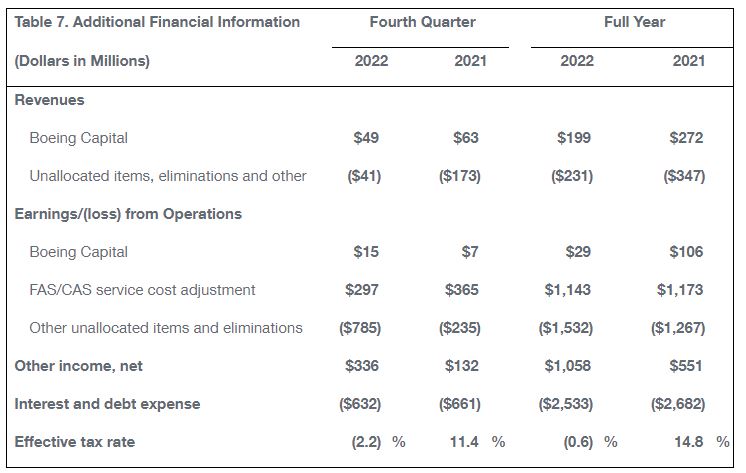
At quarter-end, Boeing Capital’s net portfolio balance was $1.5 billion. The increase in loss from other unallocated items and eliminations was driven by timing of allocations, share based compensation and deferred compensation expense. The change in other income was primarily due to increased interest rates driving increased investment income. The fourth quarter effective tax rate primarily reflects tax expense driven by an increase in the valuation allowance.
Non-GAAP Measures Disclosures
We supplement the reporting of our financial information determined under Generally Accepted Accounting Principles in the United States of America (GAAP) with certain non-GAAP financial information. The non-GAAP financial information presented excludes certain significant items that may not be indicative of, or are unrelated to, results from our ongoing business operations. We believe that these non-GAAP measures provide investors with additional insight into the company’s ongoing business performance. These non-GAAP measures should not be considered in isolation or as a substitute for the related GAAP measures, and other companies may define such measures differently. We encourage investors to review our financial statements and publicly-filed reports in their entirety and not to rely on any single financial measure. The following definitions are provided:
Core Operating Loss, Core Operating Margin and Core Loss Per Share
Core operating loss is defined as GAAP earnings from operations excluding the FAS/CAS service cost adjustment. The FAS/CAS service cost adjustment represents the difference between the Financial Accounting Standards (FAS) pension and postretirement service costs calculated under GAAP and costs allocated to the business segments. Core operating margin is defined as core operating loss expressed as a percentage of revenue. Core (loss)/earnings per share is defined as GAAP diluted earnings per share excluding the net earnings per share impact of the FAS/CAS service cost adjustment and Non-operating pension and postretirement expenses. Non-operating pension and postretirement expenses represent the components of net periodic benefit costs other than service cost. Pension costs, comprising service and prior service costs computed in accordance with GAAP are allocated to Commercial Airplanes and BGS businesses supporting commercial customers. Pension costs allocated to BDS and BGS businesses supporting government customers are computed in accordance with U.S. Government Cost Accounting Standards (CAS), which employ different actuarial assumptions and accounting conventions than GAAP. CAS costs are allocable to government contracts. Other postretirement benefit costs are allocated to all business segments based on CAS, which is generally based on benefits paid. Management uses core operating (loss)/earnings, core operating margin and core loss per share for purposes of evaluating and forecasting underlying business performance. Management believes these core measures provide investors additional insights into operational performance as they exclude non-service pension and post-retirement costs, which primarily represent costs driven by market factors and costs not allocable to government contracts. A reconciliation between the non-GAAP and GAAP measures is provided on pages 12 & 13.
Free Cash Flow
Free cash flow is GAAP operating cash flow reduced by capital expenditures for property, plant and equipment. Management believes free cash flow provides investors with an important perspective on the cash available for shareholders, debt repayment, and acquisitions after making the capital investments required to support ongoing business operations and long term value creation. Free cash flow does not represent the residual cash flow available for discretionary expenditures as it excludes certain mandatory expenditures such as repayment of maturing debt. Management uses free cash flow as a measure to assess both business performance and overall liquidity. See Table 2 on page 2 and page 14 for reconciliations of free cash flow to GAAP operating cash flow.
This press release was prepared and distributed by Boeing.








